The atmosphere is the gaseous layer surrounding the earth, it is also called air. The lower regions of the atmosphere contain gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide that are essential for plant and animal respiration. Life can be found up to approximately 2,000 meters above the earth’s surface. The atmosphere also plays critical roles in shaping the biosphere by deflecting harmful radiation from the sun and determining weather patterns.
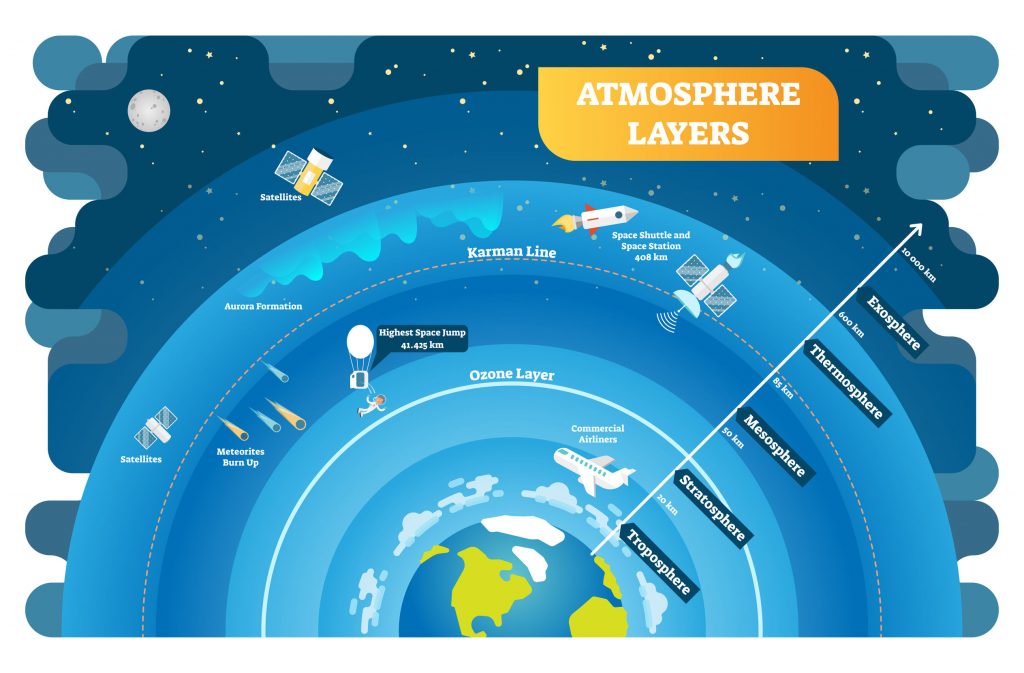
The atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the earth. It is made up of multiple layers. From the ground toward the sky, the layers of the atmosphere are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere.
Another layer is called the ionosphere and extends from the mesosphere to the exosphere. Beyond the exosphere is outer space. The boundaries between atmospheric layers are not clearly defined and change depending on latitude and season.
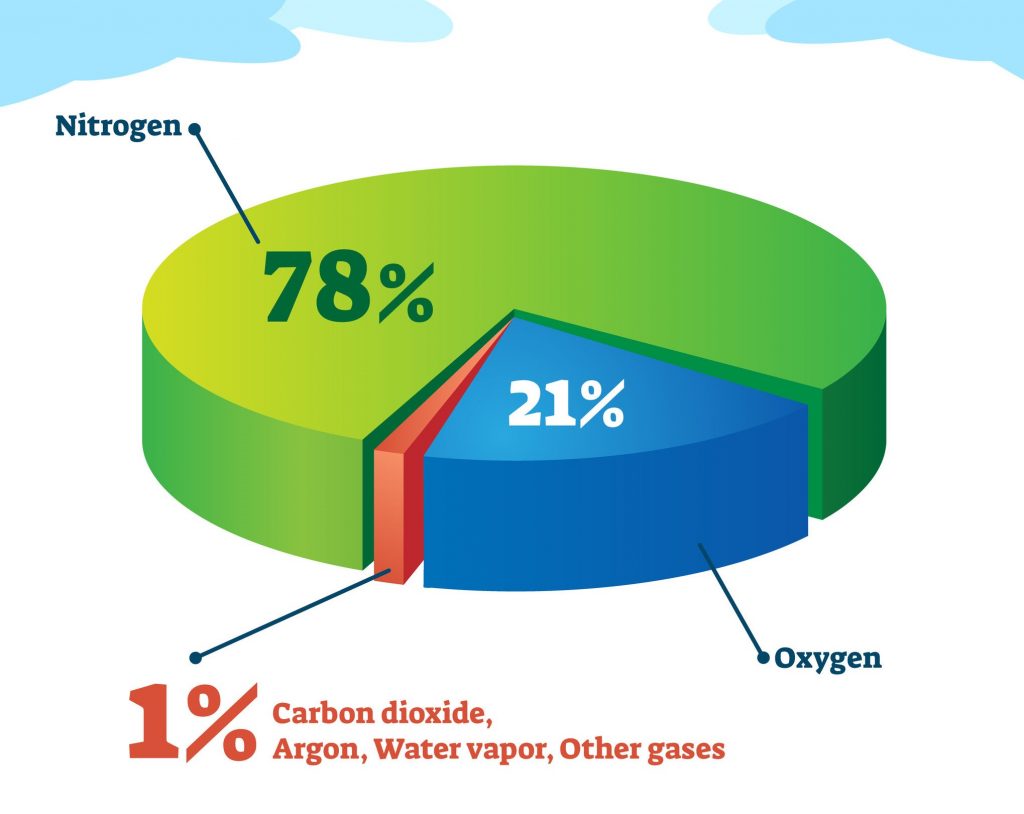
Composition of air
Nitrogen and oxygen account for 99 percent of the gases in air. Argon, carbon dioxide, helium, neon and other gases make up the remaining 1%.
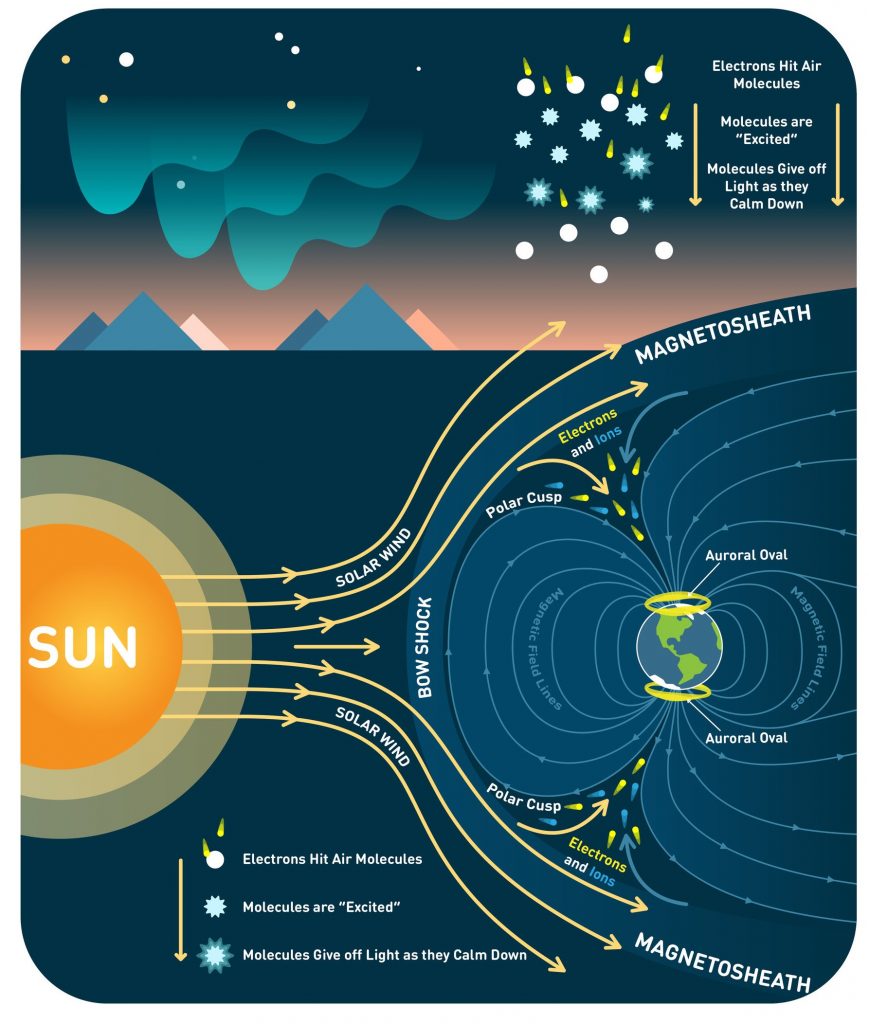
Auroras
When charged particles from the sun strike atoms in Earth’s atmosphere, they cause electrons in the atoms to move to a higher-energy state. When the electrons drop back to a lower energy state, they release a photon: light. This process creates the aurora seen at the northern and southern regions of the world.
Find out whats new for you and your students with the latest news from Australian Environmental Education
- Exploring the Underwater World
- World Wetlands Day 2025
- Violet Snails, nature’s floating marvels
- Top 10 webpages
- A Sustainable Christmas: Spreading cheer without costing the earth
Follow Australian Environmental Education on Facebook

