Life is classified into groups that start out large and become more specific in a system of classification called taxonomy. Scientists classify living things at eight different levels: domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
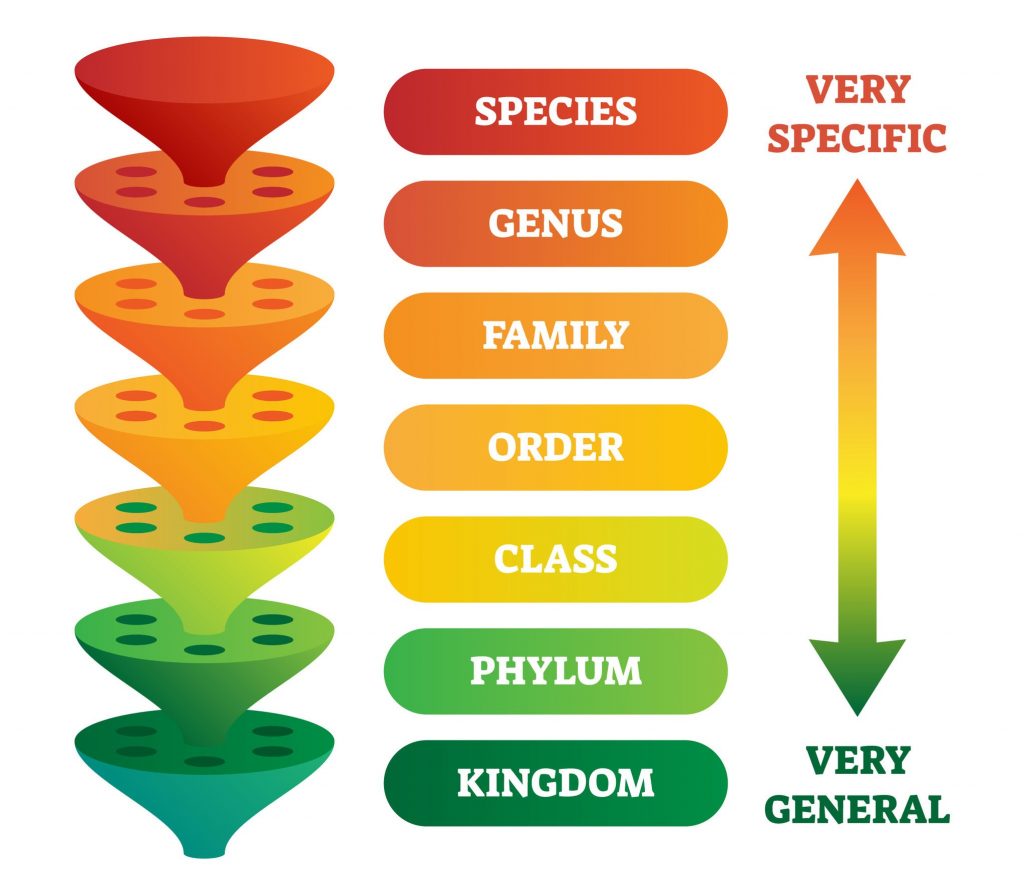
Kingdoms
There are 6 kingdoms that make up the broadest category of life. Organism are placed into kingdoms based on, cell type and the number of cells and their ability to make food. The 6 Kingdoms are:
- Plants
- Animals
- Protists
- Fungi
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria.
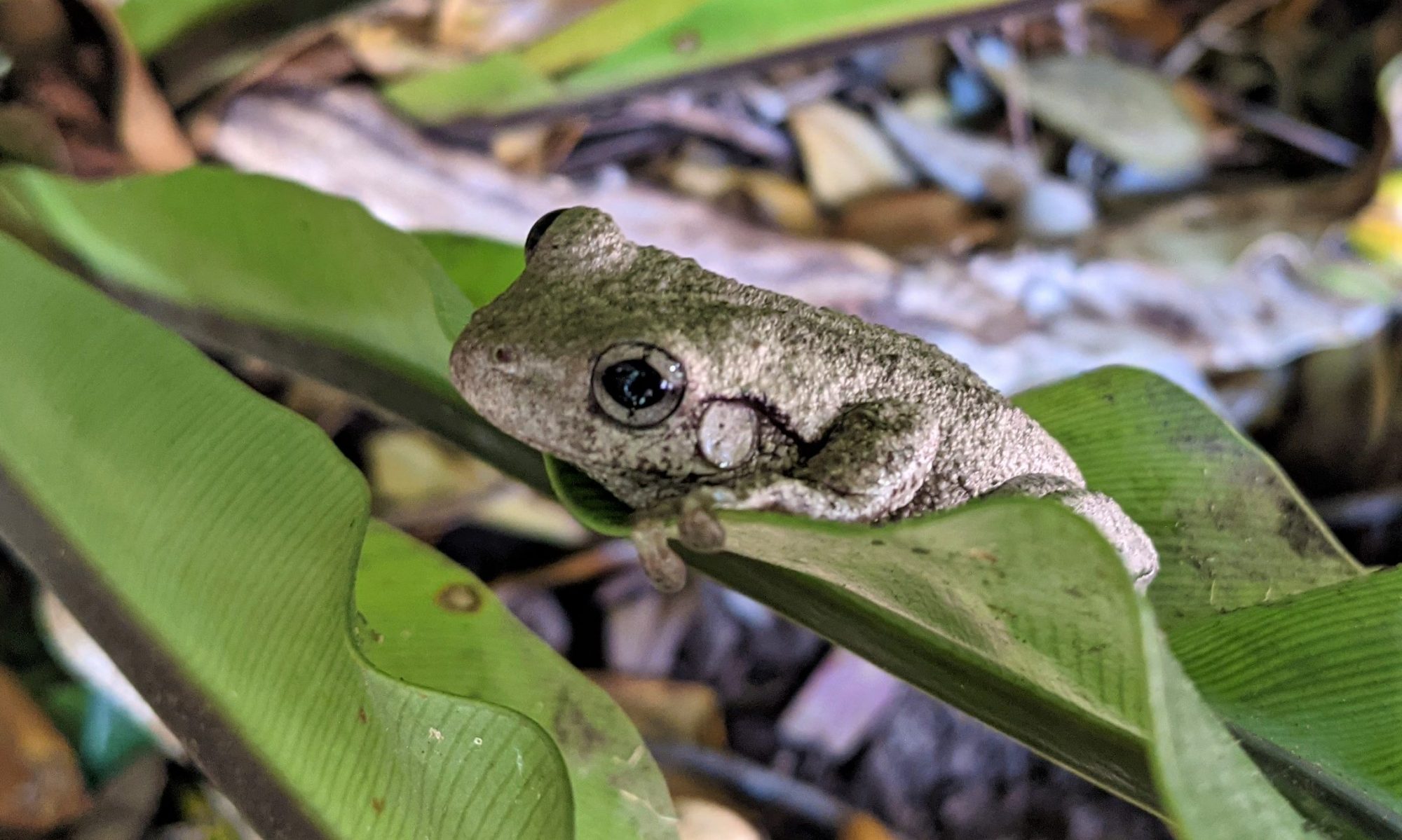
Kingdom Animalia
Life in this kingdom are multicellular eukaryotic organisms. These animals consume organic material and breathe oxygen. They are able to move, reproduce sexually and grow from a hollow sphere of cells during embryonic development. Kingdom Animalia includes all living and extinct animals species.
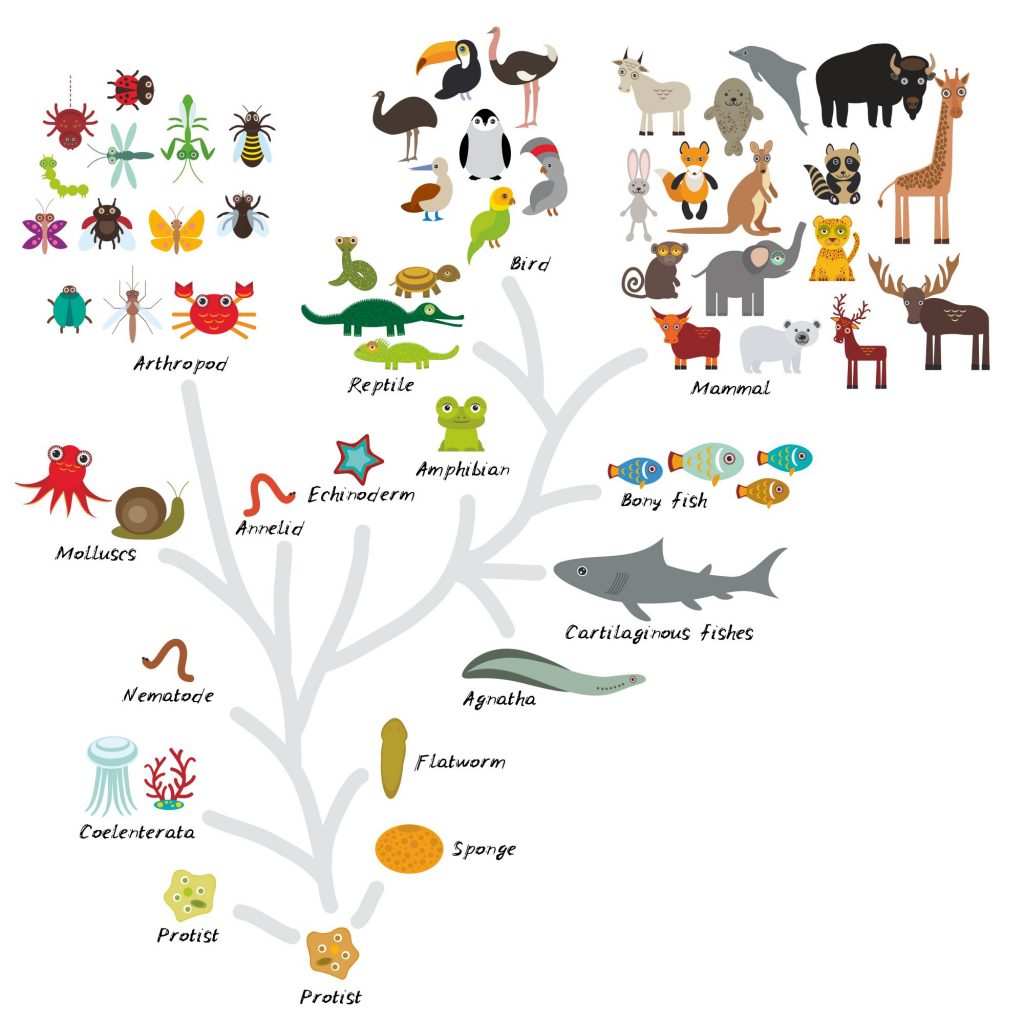
Phylum
After Kingdom the next level is phylum. Organisms in a phylum share the characteristics that distinguishes the phylum. Over time these characteristics have changed The qualities that group animals into a phylum have changed throughout scientific history, as better methods have arisen to determine how groups of animals are related.

