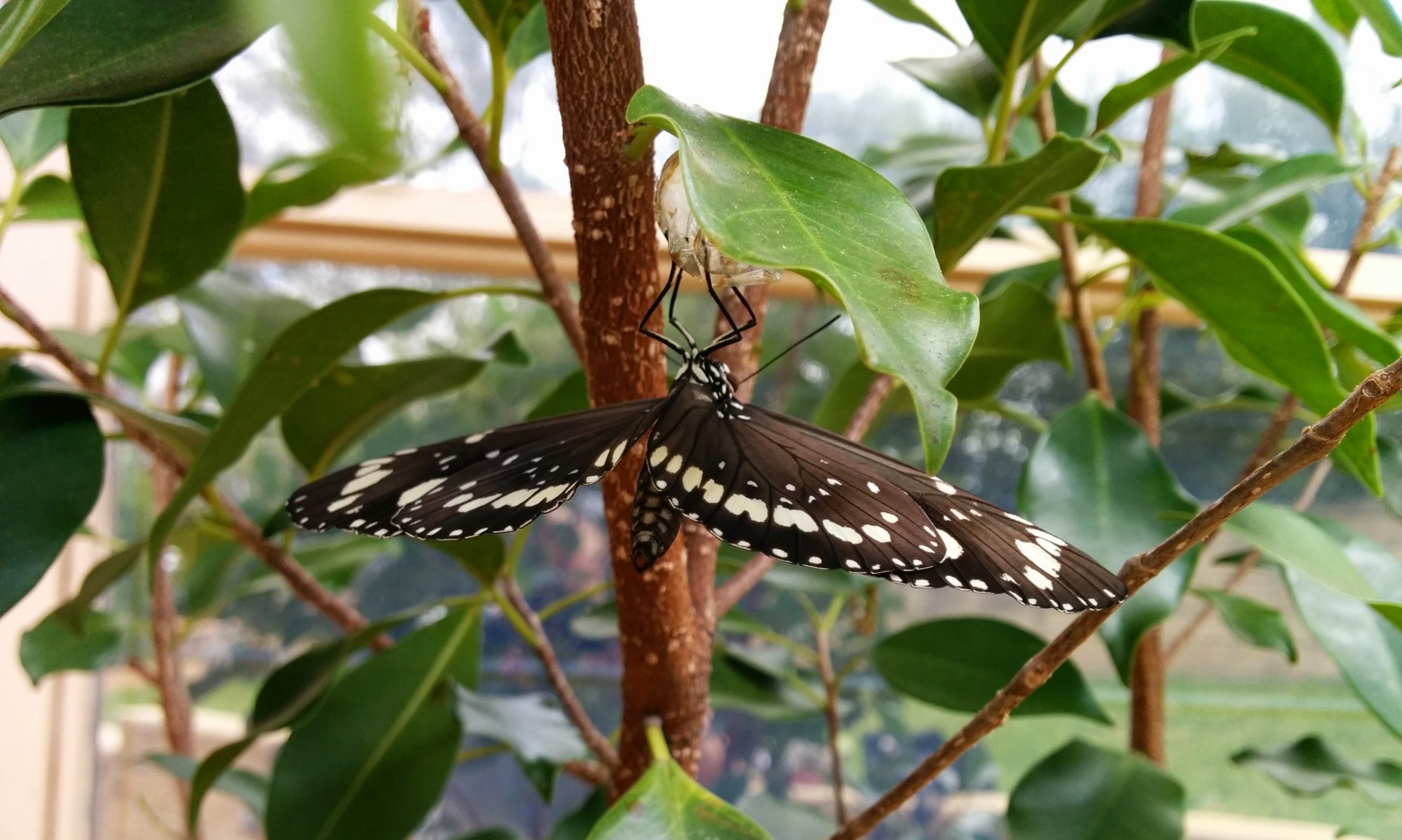
Discover more about the invertebrates living in your local area with Invertebrate Investigations. Use this information to explore your backyard and local area.
What are invertebrates
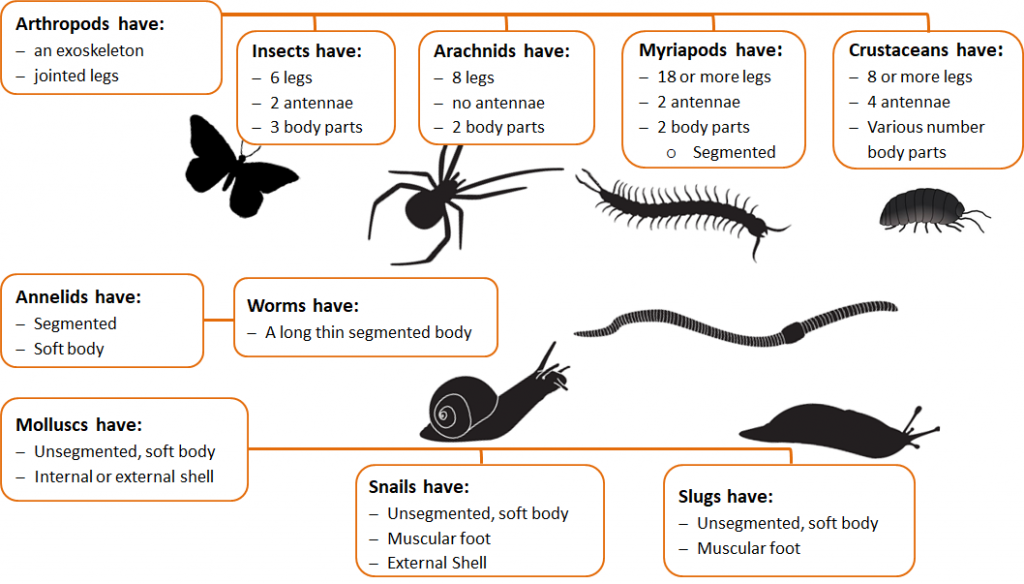
Invertebrates are animals without a backbone.
Invertebrate make up 97% of all animals on earth. Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish make up the remaining 3%. Scientist are still discovering new species of invertebrates.
Why are Invertebrates important?
Metamorphosis
A life cycle refers to the stages or changes that an animal goes through while it’s alive. There are different types of life cycles depending on the species. Vertebrates typically have three stages to their life cycle: egg, juvenile and adult. Amphibians differ to other vertebrates and undergo metamorphosis.
Find out more
We can’t often see the remarkable diversity of insect life in our gardens. Sometimes the marks and blemishes on leaves to identify which insect many be around.
Bugwise


Bugwise brings the world of invertebrates to your students, engaging them in real science in local environments. Find out what insects and spiders you are sharing your schools with and why they are vitally important to a healthy planet.
Backyard Buddies
Backyard Buddies is a free initiative run by the Foundation for National Parks & Wildlife. It gives you simple tips to transform your backyard into a safe habitat for native animals.
Backyard Buddies are the native plants and animals that share our urban areas, waterways, backyards and parks. Backyard Buddies are also the people who value native wildlife and want to protect it. Find out how you can Backyard Buddy.
Build an Insect Hotel
What sort of hotels do insects like to stay in? Build your hotel using natural materials and remember that insects range in size so creating different diameter holes will cater for everyone. Find out more below and at Backyard Buddies.
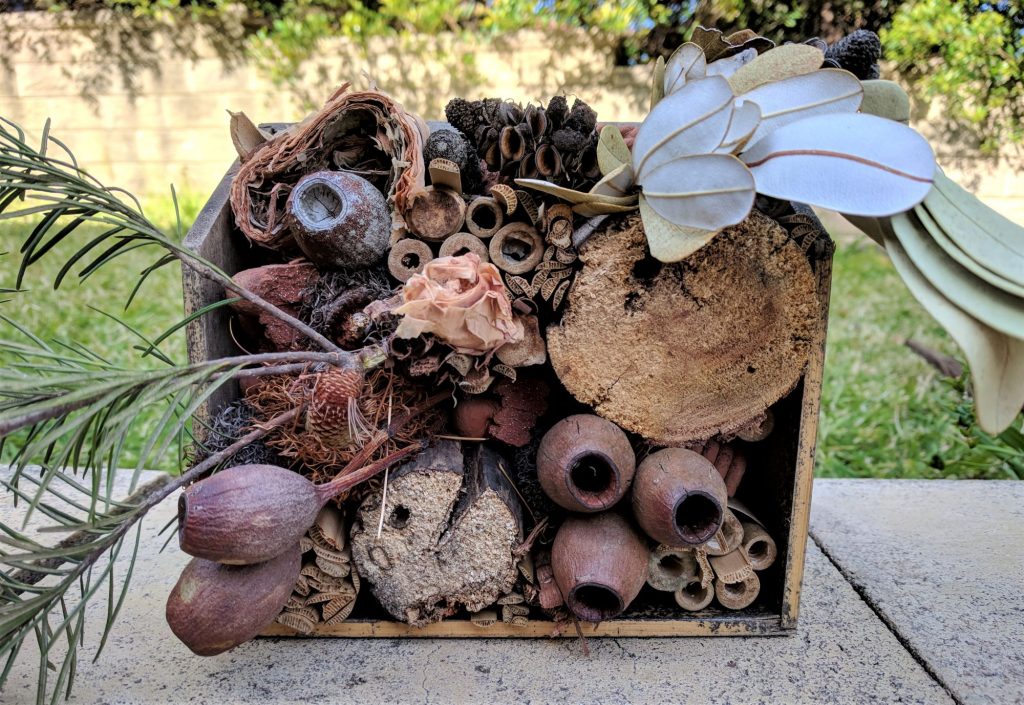
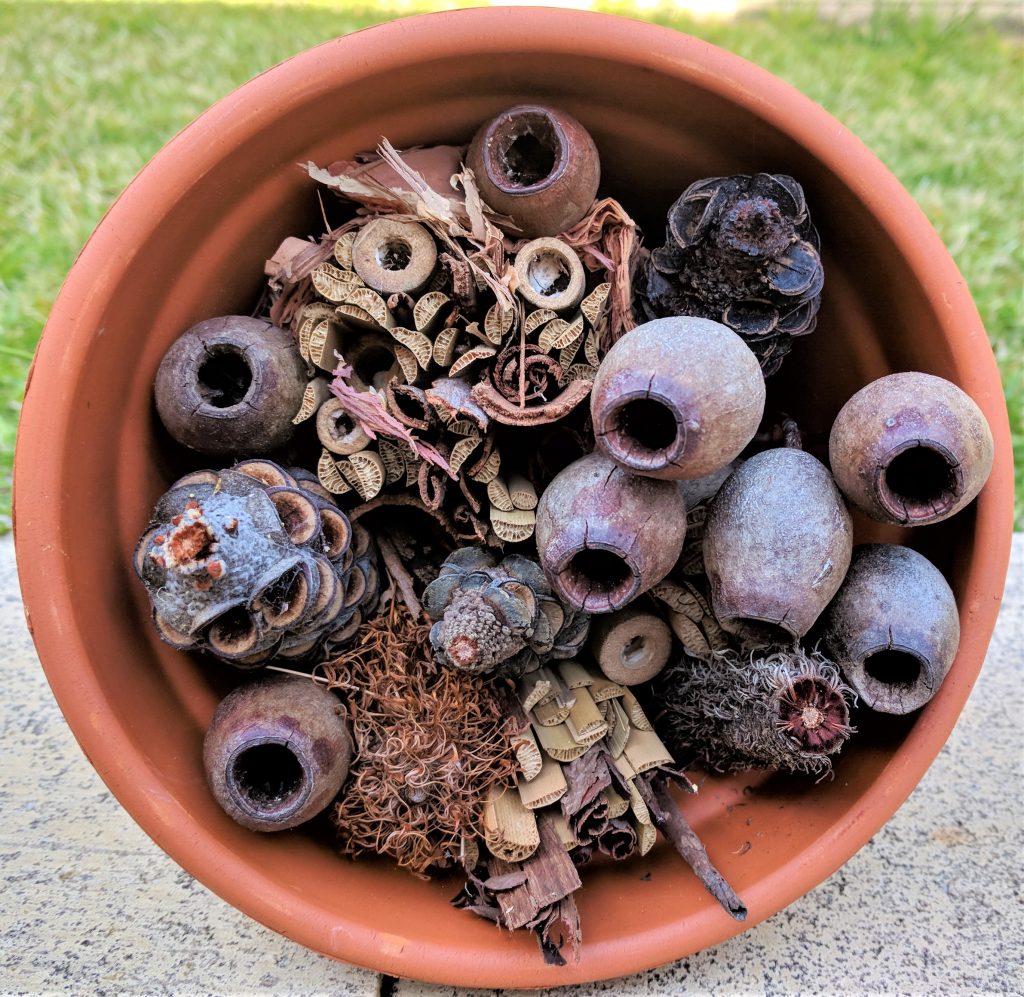


Discover what Minibeast live in your backyard
Use these techniques to discover what invertebrates call your backyard home. Use a combination to determine the diversity of invertebrates in your local area.
- Pitfall traps sampling involves placing a small container buried to ground level so that it can collect anything that falls into it. This is a commonly used technique that catches large amount of material for very little effort. Common species found with this method include ants, spiders and beetles. This test is also very easy to standardise.
- Leaf Litter sorting involves collecting leaf litter then sifting through the material to find the invertebrates. Protective clothing should be worn, sample sizes should be the same and equal lengths of time should be spent sifting the leaf litter samples.
- Beat sampling is probably the most widely used technique for collecting invertebrates from vegetation. This is a good technique for collecting beetles, ants, bugs and spiders. Use a sturdy stick is used to beat the vegetation, stunning the invertebrates. They can be collected in a light colour shallow bag or off a drop sheet.
- Dip Netting is the simplest and most effective technique for collecting aquatic invertebrates. Nets can be used to collect from shallow and reedy areas. Organisms are put in a bucket or container along with water from the creek or pond to be identified.
Find out more with these links

