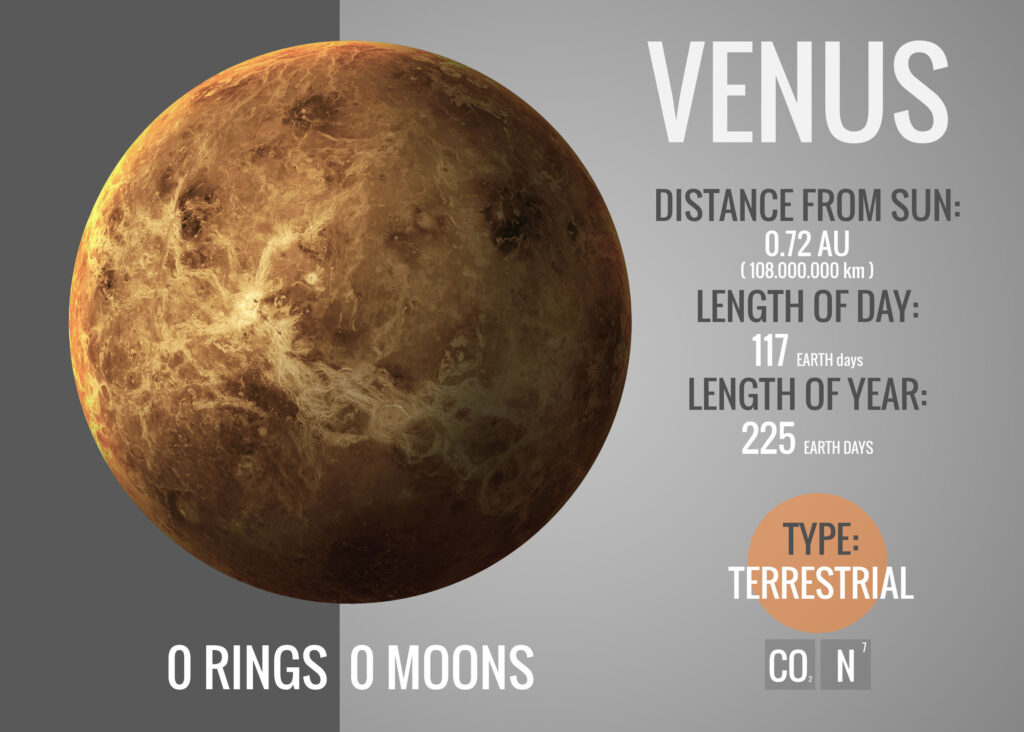
Venus is the second planet from the Sun and is often referred to as Earth’s “sister planet” due to its similar size, mass, and composition. However, its environment is vastly different.
Key Characteristics:
- Size and Structure: Venus has a diameter of about 12,104 km, slightly smaller than Earth. It has a rocky composition with a metal core, silicate mantle, and crust.
- Atmosphere: Its thick atmosphere is composed mostly of carbon dioxide (96.5%) with clouds of sulfuric acid, making it the hottest planet in the Solar System. Surface temperatures average around 475°C, due to a runaway greenhouse effect.
- Rotation: Venus rotates very slowly and in the opposite direction of most planets in the Solar System. One day on Venus (243 Earth days) is longer than its year (225 Earth days).
- Surface Features: The surface is covered with volcanic plains, large craters, and vast mountain ranges. Its lack of plate tectonics means the surface undergoes global volcanic resurfacing periodically.
Venus is one of the brightest objects in the night sky, often visible shortly after sunset or before sunrise, earning it the nicknames “Morning Star” and “Evening Star.”
Venus Exploration:
Numerous missions have been sent to study the planets surface, including NASA’s Mariner, the Soviet Union’s Venera series, and ESA’s Venus Express. Upcoming missions like NASA’s VERITAS and ESA’s EnVision aim to uncover more about the geology and climate.
Venus’s extreme greenhouse effect, potential past habitability, and unexplained atmospheric phenomena remain topics of scientific interest and study.

